Oral sessions SH/OG/HE (infomation on oral session)
Poster sessions SH/OG/HE (infomation on poster session)
ICRC2003
program
![]() Opening ceremony
Opening ceremony![]() Hess Lecture/Plenary/Highlight
sessions
Hess Lecture/Plenary/Highlight
sessions![]() Rapporteur
sessions
Rapporteur
sessions![]() Parallel sessions
Parallel sessions
Oral
sessions SH/OG/HE (infomation
on oral session)
Poster sessions SH/OG/HE (infomation
on poster session)
![]() Scientific programs
Scientific programs
28th International Cosmic Ray Conference
Main Convention Hall, Tsukuba International
Congress Center
Tsukuba, 31 July 2003
|
9:20 |
Welcoming Address |
||
|
|
|
Dr. Motohiko Yoshimura |
(Chairman of the Local Organizing Committee and Director of Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, the University of Tokyo) |
|
|
|
Dr. Hiroshi Komiyama |
(Vice president, the University of Tokyo) |
|
|
|
Dr. Kazuo Kitahara |
(President, the Physical Society of Japan) |
|
|
|
Dr. Humitaka Sato |
(Chairman, Japanese Liaison Committee for the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics) |
|
|
Official Opening of the 28th International Cosmic Ray Conference and Presentation of Awards |
||
|
|
|
Dr. Peter Wenzel |
(Chairman of Commission C4 Cosmic Rays of the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics) |
|
|
Welcoming Remarks |
||
|
|
|
Presentation of the O'Ceallaigh Medal to Prof. Frank B. McDonald |
|
|
|
|
Presentation of the Shakti P. Duggal Award to Dr. Pasquale Blasi |
|
|
|
|
Presentation of Yodh Prize to Prof. B. V. Sreekantan |
|
|
(short break) |
|
||
|
10:30 |
Hess lecture |
|
|
|
|
|
Prof. Masatoshi Koshiba |
|
|
|
|
Birth of Neutrino Astrophysics |
|
|
11:10 |
End of Opening Ceremony |
||
![]() Hess lecture/Plenary/Highlight
sessions
Hess lecture/Plenary/Highlight
sessions
|
July 31 |
Main Convention Hall |
|||
|
|
10:30-11:10 |
Hess Lecture |
||
|
|
11:40-12:10 |
highlight |
||
|
|
12:10–12:40 |
highlight |
Latest RHESSI Results on Particle Acceleration and Energy Release in Solar Flares (38.6MB) |
|
|
August 1 |
Main Convention Hall |
|||
|
|
11:05–11:45 |
plenary |
||
|
|
11:45-12:15 |
highlight |
||
|
|
12:15-12:45 |
highlight |
J. Beer |
Long-Term Solar Variability by Cosmogenic Isotopes and the Response of the Climate System |
|
August 3 |
Main Convention Hall |
|||
|
|
11:05–11:45 |
plenary |
Gravitational Radiation: Observing the Dark and Dense Universe (5.4MB) |
|
|
|
11:45-12_15 |
highlight |
E. C. Stone |
The Solar Wind Termination Shock and the Outer Heliosphere |
|
|
12:15-12_45 |
highlight |
Highest Energy Cosmic Rays and the Pierre Auger Project (7.4MB) |
|
|
August 5 |
Main Convention Hall |
|||
|
|
11:05–11:45 |
plenary |
||
|
|
11:45-12:45 |
plenary |
T. C. Weekes, T. Kifune, H. Voelk |
TeV Gamma Ray Observation and the Origin of Cosmic Rays (T.C.Weekes (8.8MB), T.Kifune (1.9MB), H.Voelk) |
|
|
18:30-20:30 |
BANQUET at Hotel Shinonome |
||
|
|
|
*After dinner address |
M. M. Shapiro |
Fifty years of cosmic ray science — a personal retrospective |
|
August 6 |
Main Convention Hall |
|||
|
|
11:05–11:45 |
plenary |
Cosmology Update: Dark Energy, Inflation, and Dark Matter (8.9MB) |
|
|
|
11_45-12:15 |
highlight |
N. Kawai |
Contribution of HETE-2 to the Progress in Understanding Gamma-Ray Bursts |
|
August 8 |
at Kashiwa |
|||
|
|
18:00-19:30 |
Public Hess Lecture |
||
|
August 7 |
Main Convention Hall |
||
|
|
09:10-09:50 |
||
|
|
09:50-10:30 |
||
|
|
10:55-11:35 |
||
|
|
11:35-12:15 |
||
|
|
12:15-12:55 |
||
|
|
14:20-15:00 |
||
|
|
15:00-15:40 |
||
|
|
16:10-16:50 |
||
|
|
16:50-17:30 |
||
In the 28th ICRC scientific program, several subsessions in ``Solar and
Heliospheric Phenomena (SH)'' are merged in new subsessions. This comes from
limited numbers of the applicants to the subsessions. Following is the current
list of subsessions in SH in comparison with the old subsessions.
Solar and Heliospheric Phenomena
(SH)
|
New subsession code |
New name |
Original subsession code |
Original name |
|
SH1 |
Sun and Corona |
|
|
|
SH1.1 |
Energetic photons and neutrons |
|
|
|
SH1.2 |
Energetic charged particles: Composition, spectra, and charge state |
|
|
|
SH1.3 |
Particle acceleration on/near Sun |
|
|
|
SH1.4 |
Ground level enhancements |
|
|
|
SH1.5 |
Instrumentation and new projects |
SH 1.6 |
Instrumentation and new projects |
|
|
|
SH 2.7 |
Instrumentation and new projects |
|
|
|
SH 3.7 |
Instrumentation and new projects |
|
SH2 |
Acceleration and Transport Phenomena in the Heliosphere |
|
|
|
SH2.1 |
Interplanetary transport of solar energetic particles |
|
|
|
SH2.2 |
Coronal mass ejections and Forbush decreases |
SH 1.5 |
Coronal mass ejections |
|
|
|
SH 2.2 |
Forbush decreases /Effects of coronal mass ejections |
|
SH2.3 |
Interaction regions, shocks, transport, and acceleration |
SH 2.3 |
Propagating interaction regions/shocks |
|
|
|
SH 2.4 |
Co-rotating interaction regions/shocks |
|
|
|
SH 2.6 |
General acceleration and transport phenomena |
|
SH3 |
Galactic and Anomalous Cosmic Rays in the Heliosphere |
|
|
|
SH3.1 |
Anomalous cosmic rays and outer heliosphere |
SH 2.6 |
General acceleration and transport phenomena |
|
|
|
SH 3.1 |
Origin and acceleration of anomalous cosmic rays |
|
SH3.2 |
Modulation models |
|
|
|
SH3.3 |
Gradients, anisotropies, spectra, and composition |
SH 3.3 |
Gradients, anisotropies |
|
|
|
SH 3.4 |
Spectra, composition, charge state |
|
SH3.4 |
Long-term variations |
SH 3.5 |
Long-term variations |
|
SH3.5 |
Long-term variation of cosmic rays studied by cosmogenic nuclides |
SH 3.5 |
Long-term variations |
|
|
|
SH 3.6 |
Terrestrial effects and cosmogenic nuclides |
|
SH3.6 |
Terrestrial effects and cosmogenic nuclides |
|
|
OG:
Cosmic Ray Origin and Galactic Phenomena
OG1:
Direct Measurements and Origin of Cosmic Rays
OG
1.1 Cosmic rays observed with balloons and satellites
OG 1.2 Cosmic ray source
composition
OG 1.3 Cosmic ray propagation
OG 1.4 Acceleration of cosmic
rays
OG 1.5 Instrumentation and new projects
OG2:
X-Ray and Gamma Ray Measurements
OG
2.1 Diffuse galactic emission
OG 2.2 Galactic sources (e.g. supernova remnants,
pulsars, binaries)
OG 2.3 Extra-galactic sources (e.g. active galactic nuclei,
clusters of galaxies)
OG 2.4 Gamma ray bursts
OG 2.5 Instrumentation and
new projects
OG3:
Gravitational Waves
OG 3.1 Gravitational
wave sources
OG 3.2 Observation and data analysis
OG 3.3 Current status
of ground based detectors
OG 3.4 R&D for advanced detectors
OG 3.5
Other related topics to gravitational wave
HE:
High Energy Phenomena
HE1:
Extensive Air Showers and UHE Cosmic Rays
HE
1.1 Air shower observation for energy < 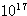 eV
eV
HE 1.2 Theory and simulations (including origins of knee)
HE 1.3
Air shower observation for energy > 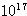 eV
eV
HE 1.4 Theory and simulations on UHE cosmic rays
HE 1.5 Instrumentation
and new projects
HE2:
Muons and Neutrinos
HE 2.1 Muon
experiments
HE 2.2 Solar, atmospheric and related neutrino experiments
HE
2.3 Neutrino telescopes
HE 2.4 Theory and calculations
HE 2.5 Instrumentation
and new projects
HE3:
Interactions, Particle Physics Aspects, Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology
HE
3.1 Hadron interactions (accelerator and cosmic ray experiments)
HE 3.2 Proton
decay and new phenomena: experiments and theory
HE 3.3 Dark matter, astroparticle
physics and cosmology
HE 3.4 Instrumentation and new projects
Back
to ICRC2003 main page